The Hidden Shift in GLP-1 Drug Market Dynamics: Emerging Disruption from Patent Expirations and Regulatory Changes
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) such as semaglutide and tirzepatide have revolutionized treatment in metabolic diseases, notably obesity and type 2 diabetes. While their blockbuster revenue projections dominate headlines, a quieter but equally significant disruption is emerging: the interplay of upcoming patent expirations, evolving regulatory frameworks, and shifting market competition. This weak signal could reshape pharmaceutical production, pricing power, and even influence healthcare access in the next decade.
What’s Changing?
On the surface, the GLP-1 drug market booms. By 2030, combined sales of semaglutide and tirzepatide variants may reach over $100 billion annually, driven by their expanded indications beyond diabetes to weight loss and cardiometabolic risk reduction (The Peptide List).
Yet beneath this growth, several subtle but crucial shifts are unfolding that could disrupt this upward trajectory:
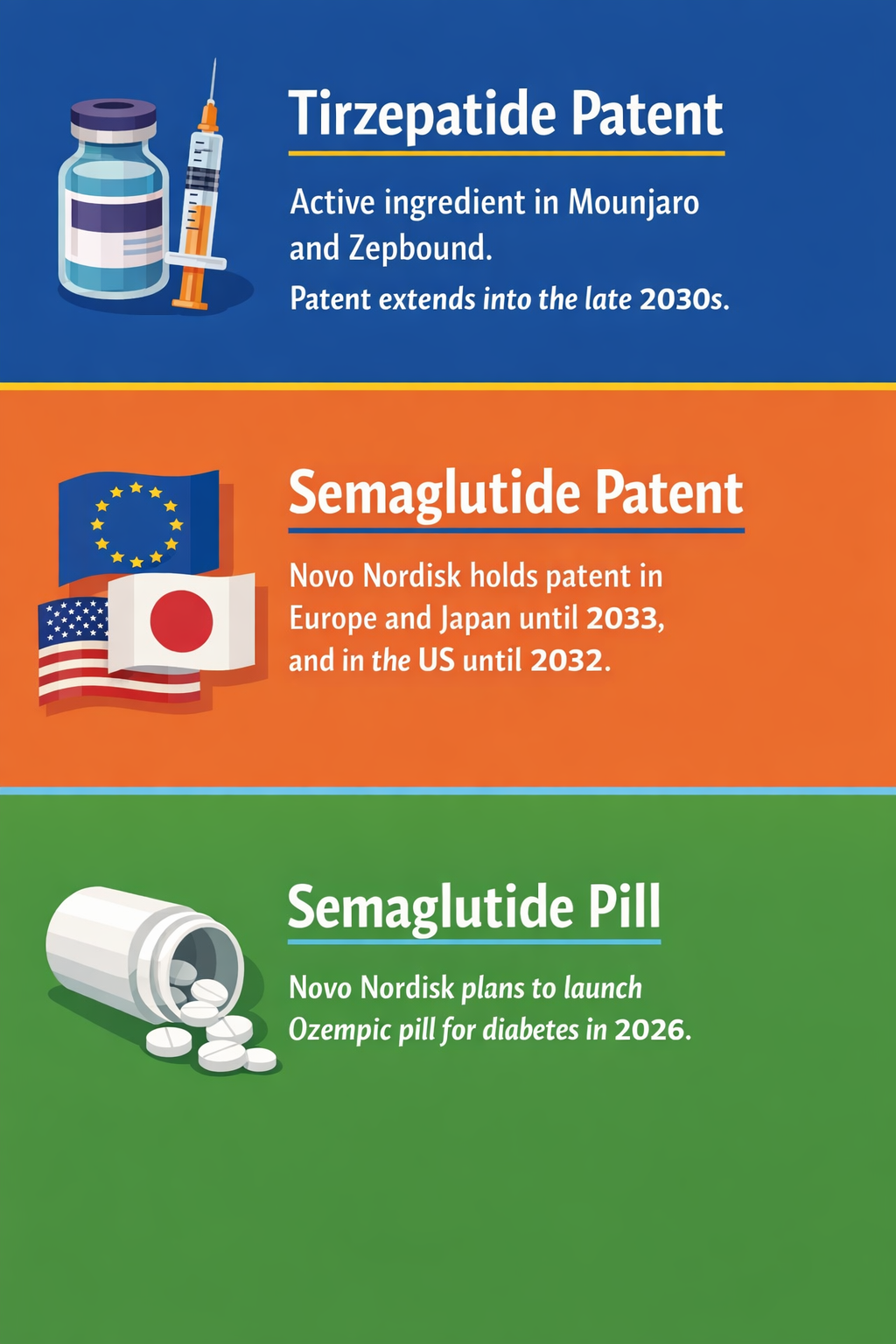
- Patent Expirations and Extended Protection Windows: Semaglutide faces patent expiration in the U.S. from 2026 onward but retains protection in Europe and Japan until 2032-2033 (The Guardian). Tirzepatide’s patent extends into the late 2030s (CNBC), allowing sustained exclusivity beyond semaglutide’s period of vulnerability.
- Emerging Generic and Compounded Competition: As key semaglutide patents expire, the compounding industry looks to increase supply of GLP-1 formulations. However, stricter FDA controls over active ingredients in compounded drugs aim to limit unregulated versions, casting uncertainty over how this segment evolves (Scientific American).
- Route-of-Administration Diversification: Novo Nordisk is expanding into oral semaglutide formulations for diabetes with plans for a 2026 launch of the Ozempic pill (Yahoo Finance). Lilly’s oral GLP-1 candidate, orforglipron, is projected to tap into $11.8 billion market potential (Drug Discovery News), signaling a shift from injectable-only therapies.
- Pricing and Supply Pressures Impacting Sales Forecasts: Despite optimistic revenue projections, Novo Nordisk anticipates a possible 5–13% sales decline in 2026 due to pricing competition and manufacturing bottlenecks for Wegovy (Chronicle Journal).
- Market Segmentation and Therapeutic Extension: The metabolic franchise is broadening beyond type 2 diabetes to obesity and cardiometabolic risk reduction, pushing GLP-1 use into preventive care and chronic disease management, which may change payer dynamics and patient populations (Yahoo Finance).
These developments form a complex, interwoven landscape that suggests the GLP-1 market will not simply expand linearly but undergo structural transformations with varying impacts depending on geography, regulation, and therapeutic niche.
Why is this Important?
The conventional narrative highlights GLP-1 drugs as a lucrative, unassailable growth opportunity for pharmaceutical companies. However, the slow but certain convergence of patent cliffs, regulatory tightening, and production bottlenecks may fracture this outlook in ways few strategists currently anticipate.
Firstly, patent expirations often herald the entrance of generics and biosimilars that disrupt pricing power. While the semaglutide patent expiry in the U.S. might suggest a swift decline in cost and increased availability, the concurrent tightening of FDA regulations on compounded formulations could restrict unlicensed market entries, delaying or limiting affordable alternatives. This tension introduces unpredictability in market access and pricing.
Secondly, emerging oral GLP-1 drugs could reshape treatment paradigms by enhancing patient compliance and expanding indications. This could intensify competition not only among pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly but also among drug delivery platforms, thereby changing investment, manufacturing, and marketing strategies.
Thirdly, manufacturing capacity constraints and pricing pressures forecasted for 2026 may signal systemic supply chain vulnerabilities. These could impact global markets unequally, especially in less affluent regions where access to injectable drugs is challenging. This drives questions about equitable distribution and the role of government policy in shaping access.
Finally, the expansion of GLP-1 drugs into preventive and broader cardiometabolic uses creates new decision frameworks for healthcare providers, insurers, and regulators. Strategic planning in healthcare systems could pivot to managing chronic conditions earlier, affecting resource allocation and reimbursement models.
Implications
The unfolding dynamics imply several significant implications across industries and sectors:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Companies may need to balance innovation with lifecycle management strategies, focusing on formulation diversification (oral vs injectable), patent portfolio extensions, and navigating regulatory landscapes. Firms might accelerate R&D for next-generation GLP-1 analogs or combination therapies to maintain market share beyond patent expiry.
- Regulators and Policymakers: The FDA’s evolving stance on compounded GLP-1 drugs signals growing regulatory scrutiny. Policymakers must balance drug safety and quality with ensuring market competition does not unfairly limit access. International regulatory harmonization could become more important due to staggered patent protections by region.
- Healthcare Providers and Payers: Expansion into preventive cardiometabolic uses may alter clinical guidelines and reimbursement policies. Providers might face decisions about integrating oral GLP-1 therapies into treatment protocols, potentially improving adherence but adding complexity to formularies.
- Supply Chain and Manufacturing: Production bottlenecks may become critical constraints. Investment in manufacturing scale-up, process innovation, and supply chain resilience will be needed—both from pharmaceutical producers and from contract manufacturing organizations supporting them.
- Patients and Public Health: Access disparities could widen if high costs and regulatory hurdles restrict availability to specific regions or socioeconomic groups. Public health initiatives may need to address these gaps, possibly through subsidy programs or alternative therapeutic access mechanisms.
Strategic foresight must consider not just headline revenue projections but the nuanced ecosystem shifts emerging through patent timelines, regulatory frameworks, and technology transitions.
Questions
- How will generic and biosimilar entries into the GLP-1 market balance with FDA regulatory standards and compounding restrictions to affect drug pricing and accessibility?
- What strategic advantages might oral GLP-1 formulations confer, and how will this affect competitive positioning among pharmaceutical companies and health systems?
- How could possible manufacturing bottlenecks reshape supply chains, and what redundancies or innovations could mitigate these risks?
- In what ways might expanding GLP-1 indications into preventive cardiometabolic care alter payer strategies and public health outcomes?
- How might differences in patent expiration across regions influence global market dynamics and patient access?
Keywords
GLP-1 drugs; semaglutide; tirzepatide; patent expiration; FDA regulation; oral drug formulation; manufacturing bottlenecks; metabolic disease; healthcare access
Bibliography
- The 2026 peptide outlook: five next big things. The Peptide List. https://thepeptidelist.substack.com/p/the-2026-peptide-outlook-five-next
- Why the FDA is cracking down on compound GLP-1 drugs for weight loss. Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/why-the-fda-is-cracking-down-on-compound-glp-1-drugs-for-weight-loss/
- Novo Nordisk’s turnaround story and risk factors. Yahoo Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/novo-nordisks-turnaround-story-risk-145400550.html
- In 2026 drug discovery faces a higher bar. Drug Discovery News. https://www.drugdiscoverynews.com/in-2026-drug-discovery-faces-a-higher-bar-16997
- Marketminute 2026: Eli Lilly projects record revenue as metabolic franchise decouples from competition. Chronicle Journal. http://markets.chroniclejournal.com/chroniclejournal/article/marketminute-2026-2-6-eli-lilly-projects-record-80b-83b-revenue-for-2026-as-metabolic-franchise-decouples-from-competition
- Novo Nordisk plans to launch semaglutide pill Ozempic later in 2026. Yahoo News Canada. https://ca.news.yahoo.com/health-matters-novo-nordisk-plans-175720434.html
- Wegovy, Ozempic forecast and patent protection timelines. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/business/2026/feb/04/wegovy-ozempic-forecast-revenue-share-price-drop
- Raising price target on Eli Lilly as GLP-1 leader delivers. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2026/02/04/were-raising-our-price-target-on-eli-lilly-as-the-glp-1-leader-delivers.html